Just Tell us Your Idea, Zetar Can Make It Come True.
From Mold Design to Mold Making
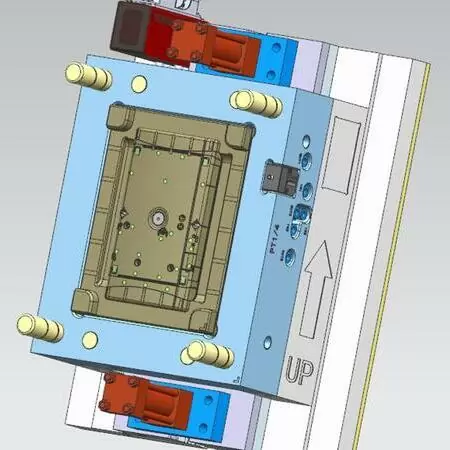

Injection Mold Making Services
- Zetar offers complete injection mold making services as well. Featuring in-house tool fabrication, Zetar can turn around your urgent needs quickly and get it to market fast with our experienced molds makers meeting all of the custom specifications you need using such applications like Mold Technology, VDI Standard or High Polish SPI type requirements.
Injection Mold Making Process Flowchart

Order
When Ordering is confirmed, information is gathered

Working Schedule
Scheduling of all machining processes involved in the injection mold

Mold Design
Injection mold design is done by experienced engineers

Milling & Lathe
Milling and lathe is a practicable method for injection molds

Steel Material Purchasing and inspection
Order Steel Mold Base and steel inspection

Mold design Approval
Injection mold design is approved after the work is viewed and discussed

CNC Milling
Rough CNC Process and Precision CNC process

EDM
EDM does some small, deep and thin structures.

Grinding and Polishing
Grinding and polishing are to smooth and to shine the surface treatment

Delivery
Export injection molds are packed and delivered on-time

Quality Control
CMM plays an important role for QC part

Fitting and Assembly
Fitting and assembly is to assure parts are fit properly
The Injection Mold Making Process: A Complete Walkthrough
Injection mold making is a complex and multifaceted process that requires precision, attention to detail, and the use of specialized materials.
Table Of Contents
What is plastic injection mold?
Injection mold is a tool that can be used to reproduce a specific shape in large quantities by forcing a heated semi-liquid plastic material into the mold cavity through an plastic injection molding machine.
Designed as a hollow metal block with cavities, The molten plastic is forced into the cavities of the mold, where it takes on the desired shape.
Though you may not see them shown in the following figure, in fact, there are multiple holes made inside the plastic injection molds to realize temperature control by way of oil, water or heaters.
This is important because the plastic material will solidify at different rates depending on the temperature. In order to ensure that all the material is solidified properly and that the final product is consistent, it is necessary to maintain a consistent temperature throughout the plastic injection molding process.


What are the components of injection mold?
The mold halves of the injection mold work like this:
Cavity (A Side): The cavity is the side of the mold that creates the cosmetic part. It’s often referred to as the A side of the plastic injection molds.
Core (B Side): The core is usually the interior or noncosmetic side of the part. The core side also contains the ejection mechanism that pushes the completed part out of the mold.
The most common style is the straight-pull mold. This injection mold has two halves, a core and a cavity. The core is the raised half of the mold. It provides support for the other side, which is called the cavity. This cavity holds space for the final product to be injection molded.
The mold halves usually made from steel or aluminum, are held together in the molding press by mechanical clamps or hydraulic pressure. This creates a tight seal that prevents the molten plastic from escaping. When the plastic has cooled and hardened, the clamps or pressure is released and the mold is opened. The halves are then separated and the finished product is removed.

Mold Base
The mold core and mold cavity are each mounted onto the mold base, which is then fixed to platens inside the plastic injection molding machines.
This plastic injection molding machines clamps the two together tightly to create a strong seal that prevents any leakage of plastic. When this process is complete, the finished plastic parts can be taken out of the injection molds.

The front half or the cavity side of the mold base includes
- The Support plate – used to mount the mold and stabilize it
- The locating ring – aligns the mold base with the nozzle
- The Sprue bushing – helps material flow from the nozzle and to the part
- Runner – passes material like plastics, rubber, and thermoplastic material from the sprue to where it will be injected into a cavity in a mold
The rear half or the cavity side of the mold base includes
- Support plate – used to mount the mold and stabilize it
- Ejection system – Pushes the finished plastic parts out of the mold. This system is made up of several parts: the ejector bar, the ejector plate, the ejector pins and the ejector box.
Runner System
A runner system directs melted plastic into the mold. Designing the runner is as important as designing the injection molded part. When designing a runner system, you need to take into account the following factors:
Resin Type – You need to select the right resin for the job. The wrong plastic material can cause problems like flash (excess material around the part) and burnout (where the plastic is so hot that it starts to melt the mold).
Mold Temperature – You need to make sure that the plastic material will solidify at the correct temperature. If it cools too quickly, you’ll get problems like cold shots (where part of the mold doesn’t fill properly).
Part Size and Weight – The heavier and larger the part, the more difficult it will be to eject from the mold. You’ll need a stronger ejection system to get.
The molten plastic that solidifies inside these runners is attached to the part and must be separated after the part ejects from the mold.
However, hot runner systems independently heat the channels, which melts the contained material and makes it easy to remove from the part.
The Cold Runner systems usually consist of Sprue, Runners, Gates:

- Sprue –The sprue is the starting point for the molten material. It is typically larger than the rest of the system to encourage proper flow. The resin flows through the sprue and into the runner system, which directs it into the mold cavities.
- Runners – Runners are the system that helps move resin from the sprue into each cavity in a mold. They do this by using a precise design that allows for even flow while using as little plastic resin as possible.
- Gates – At the end of each runner. The metal pieces for the mold that make up the A side and B side of the mold each have gates where they meet on both sides of the mold. Each gate helps to direct flow from one side to another and guides it into the correct cavity in your new plastic parts.
Gates
Gates are important because they direct the flow of plastic resin. This helps to ensure that the resin is evenly distributed throughout the mold and that the part is correctly formed.
If the gates are not designed correctly, the plastic parts can be defective. Proper resin flow is essential for the creation of defect-free plastic parts. This makes the gate design an important part of the overall mold design. Below are a few examples of gate types:
Slide – Slide gates are a popular choice for both accuracy and functionality. It’s a stationary gate that travels with the part while it’s being ejected from the mold. The design requires a precise flow that may result in delays or broken parts if not done correctly.
Pinch – Pinch gates are used for automation because they provide an easy way to inject molten material into cavities. They’re designed to pinch off material at the ejection point and direct it into the mold without overflow.
Edge – Edge gates inject plastic into the cavity through the edge of the part. This type of gate is used when the flow of material isn’t needed to be at all angles, but towards one direction.
- Tunnel – Tunnel gates are a popular choice for both accuracy and functionality. They’re designed to inject the molten resin into the cavities from a port that’s cut into the core side of the mold. This type of gate is accurate and helps to avoid problems with plastic resin flow.
Cooling System

A cooling system helps to quickly cool the molten plastic and solidify it into a part. This prevents defects like warping and shrinkage. A cooling system also helps to eject the part from the mold. There are three types of cooling systems:
Water – Water is a popular choice because it’s easy to use and helps to cool the plastic quickly. However, water can cause problems like rust and corrosion.
Air – Air is a popular choice because it’s easy to use and helps to cool the plastic quickly. However, air can cause problems like flash (excess material around the part) and burnout (where the plastic is so hot that it starts to melt the mold).
Chillers – Chillers are a popular choice because they’re accurate and can help to avoid problems with other cooling systems. However, chillers are expensive and require a lot of maintenance.
The type of cooling system that you choose is important for the success of your injection molded parts. It’s essential to select a system that will quickly cool the plastic and solidify it into a part.
What points that need to be considered before injection mold making?
There are a few important points that need to be considered when designing or manufacturing a plastic injection mold. These include:
Part tolerances: This measures how accurately the part needs to be made relative to the original design.
Draft: This is the angle at which the walls of a cavity taper, which allows for easier ejection of the part from the mold.
Ejection: This is how well the part can be After being cooled, the mold opens, and the injection molded parts will be further ejected by a push on the ejector plate by the ejector rod of the plastic injection molding machine
Why we choose plastic injection mold
There are a few reasons why plastic injection molding is a popular choice for producing injection molded parts:
High Precision: The high precision of injection molding processes is an important feature for producing plastic injection molded part. It allows plastic injection molded part manufacturers to create parts that are accurate to the original design. As a matter of fact, the precision of the finished products can be kept within 0.005in tolerance.
Cost-Effective: Injection molding processes is an economical way to mass production because it requires less labor and tooling than other manufacturing processes. This simplifies the injection molding process and makes it easier to create products with low cost.
High efficiency: One of the main reasons why plastic injection molding is such a popular choice is because it is a very fast process. This makes it an ideal choice for injection molding manufacturers who need to mass production quickly and efficiently.
The standard of plastic injection mold
Mold Steel
ASSAB – This steel is made in Sweden and is known for its high quality. It’s often used for medical devices and aerospace applications.
DAIDO – This steel is made in Japan and is known for its high quality. It’s often used for medical and aerospace applications.
FINKL – This steel is made in America and is known for its high quality. It’s often used for medical and aerospace applications.
AUBERT & DUVAL – This steel is made in France and is known for its high quality. It’s often used for medical and aerospace applications.
LKM (China)-LKM is a steel manufacturer located in China. It is known for its high quality steel, which is often used for medical and aerospace applications.
Mold Base
EMP, DME, HASCO, FUTABA, LKM.
EMP – EMP is a German company that produces high-quality mold bases.
DME – DME is an American company that produces high-quality mold bases.
HASCO – HASCO is a German company that produces high-quality mold bases.
FUTABA – FUTABA is a Japanese company that produces high-quality mold bases.
LKM (China) – LKM is a Chinese company that produces high-quality mold bases.
Hot Runner
MOULD MASTER, SYNVENTIVE, HASCO, DME, YUDO, INCOME
Latch Lock
DAIDO, HASCO, STRACK, RABOURDIN
Standard Parts
DME, HASCO, LKM, HEB, STRACK, OPITZ
Texture
VDI 3400, Mold-tech, Yick Sang, Tanazawa etc
The whole process of plastic injection mold making
How long does it take to make an injection mold?
The amount of time that it takes to manufacture a plastic injection mold depends on the type and size of part. The manufacturing process can be as little as two weeks for simple plastic parts.
At Zetar, 80% of the molds can be completed within 25-35 days, but more complex molds will require significantly longer times like 40-60days. It’s important to consider how quickly you need your injection molds so that you can plan accordingly.

Our expertise is here to serve you
phone
0086-13564311131
Sales Office: No.29 Moyu Road, Jiading District, Shanghai, China
Shanghai Factory Address: No.998 Huazhi Road, Qingpu District, Shanghai, China
Jiangsu Factory Address: No.777, Jimingtang South Road, Kunshan City, Jiangsu Province
Zhejiang Factory Address: No.1 Xingcheng Road, Yuyao City, Zhejiang Province
Zetar Industry Co.,Ltd
info@zetarmold.com
phone
0086-21-64028287

